-
1 × 45,000UGX
-
1 × 5,000UGX
-
1 × 200,000UGX
-
1 × 15,000UGX
-
1 × 60,000UGX
-
3 × 200UGX
-
1 × 1,100UGX
-
1 × 28,000UGX
-
1 × 3,500UGX
-
1 × 45,000UGX
-
1 × 800UGX
-
1 × 10,000UGX
-
1 × 10,000UGX
-
1 × 215,000UGX
-
1 × 500UGX
-
1 × 145,000UGX
-
1 × 40,000UGX
-
1 × 45,000UGX
-
1 × 190,000UGX
-
1 × 15,000UGX
-
1 × 24,000UGX
-
1 × 15,000UGX
-
1 × 70,000UGX
Rocket Health Laboratory, an online laboratory in Kampala, provides affordable, efficient, and convenient laboratory services whereby professional technicians collect samples from the comfort of one’s home or workplace, and accurate results are sent via email. Rocket Health Laboratory is an excellent choice for those looking for a reliable laboratory.
- Quantity of product Aspirin 75mg Tablet Ecorin 10's can not be less than 10
- Quantity of product Telvas H 80/12.5 Tablets 10's can not be less than 10
- Quantity of product Dutasteride/Tamsulosin 0.5/0 Duodart Capsules 30's can not be less than 10
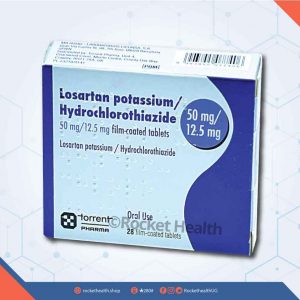
- Quantity of product Losartan Potassium 50mg Tablet Losacar 7's can not be less than 10
- Quantity of product Amlodac 5 Tablets 10's can not be less than 14
- Quantity of product Levocetirizine+Montelukast 5/10mg Breathezy-L tablet 10'S can not be less than 10
- Quantity of product Losartan 50mg & Hydrochlorothiazide 12.5mg Co-Losar Denk can not be less than 14
-
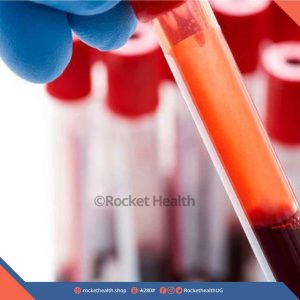
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Test (PTT)
This is a screening test that helps check a person’s ability to properly form blood clots.
Blood.
None however, a high-fat meal before the blood draw may affect the test and should be avoided.
The partial thromboplastin time (PTT; also known as activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)) is a screening test that helps evaluate a person’s ability to appropriately form blood clots. It measures the number of seconds it takes for a clot to form in a sample of blood after substances (reagents) are added. A prolonged PTT means that the blood is taking too long to form a clot, this may be caused by conditions such as liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, or a coagulation factor deficiency (e.g., factor VII deficiency).
30,000UGX -
Anti Streptolysin O Titre
This is a blood test that checks for effects of a recent streptococcus bacteria infection that may cause Rheumatic fever or kidney disease.
Blood.
You may be instructed not to eat six hours before the test. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Antistreptolysin O (ASO) is an antibody targeted against streptolysin O, a toxic enzyme produced by group A Streptococcus bacteria. Group A Streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes) is the bacterium responsible for causing strep throat and a variety of other infections, including skin infections (pyoderma, impetigo, cellulitis). In most cases, strep infections are identified and treated with antibiotics, and the infections resolve. When a strep infection does not cause identifiable symptoms and goes untreated, or is treated ineffectively, complications namely rheumatic fever and a type of kidney disease (glomerulonephritis), can sometimes develop, especially in young children.
30,000UGXAnti Streptolysin O Titre
30,000UGX -
Prothrombin Time (INR)
The prothrombin time (PT) is a test that helps evaluate your body’s ability to appropriately form blood clots.
Blood.
None needed, however if you are receiving anticoagulant therapy, the blood sample should be collected before taking your daily dose.
A PT measures the number of seconds it takes for a clot to form in your sample of blood after substances (reagents) are added. The PT is often performed along with a partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and together they assess the amount and function of proteins called coagulation factors that are an important part of proper blood clot formation. For people taking warfarin, most laboratories report PT results that have been adjusted to the INR. A prolonged PT means that the blood is taking too long to form a clot, this may be caused by conditions such as liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, or a coagulation factor deficiency (e.g., factor VII deficiency).
35,000UGXProthrombin Time (INR)
35,000UGX -
Rota Virus
The rotavirus test is a stool test used to diagnose a rotavirus infection which causes vomiting and diarrhoea especially in children.
Stool.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Rotavirus is a viral organism that affects the intestines and causes vomiting and diarrhea. This infection is especially common in young children, but it can affect adults, too. A rotavirus infection causes a condition called viral gastroenteritis. Rotavirus passes easily from person to person. It can also be picked up by touching a surface contaminated by someone with rotavirus. Sharing food or drink with an infected person can also spread it. Most people don’t need treatment for rotavirus, but it’s still important to diagnose the infection and watch for signs of dehydration.
35,000UGXRota Virus
35,000UGX -
Serum Crag
Serum Crag is a test that detects cryptococcal antigen (abbreviated “CrAg”) in blood, an indicator of cryptococcal meningitis infection.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Cryptococcal infection usually presents as meningitis, which is a swelling of the meninges,the tissues that protect the brain and spinal cord. It is caused by C. neoformans which enters the human body via the respiratory tract. Elimination of C. neoformans is through cell mediated immunity, with the participation of neutrophils, macrophages and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. In the face of immunodeficiency(HIV infection, pregnancy etc), control of the infection fails, the fungus may then disseminate to the central nervous system or other organs. Definitive diagnosis is confirmed by the culture of specimens, often the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or blood, and sometimes in respiratory secretions The condition requires hospitalization and treatment with the intravenous (IV) antifungal medication amphotericin B.
35,000UGXSerum Crag
35,000UGX -
ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST
This test enables diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes in pregnant women.
Blood.
Inform your doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test. The individual undertaking the test should fast for 12 hours prior to the test and have a meal with at least 75 gms of carbohydrates. After the meal, the patient should not take any food before having the test. Take rest for two hours during the waiting period and do not work or strain yourself because exercise may sometimes increase the blood sugar levels. If you are pregnant then there is no need to fast.
Glucose is the primary energy source for the body’s cells and the only energy source for the brain and nervous system. A steady supply must be available for use, and a relatively constant level of glucose must be maintained in the blood Postprandial blood sugar test is used to measure the amount of glucose present in our blood, after two hours of eating. This test indicates how your body responds to sugar and starch after you have a meal.
40,000UGXORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST
40,000UGX -
Creatinine Kinase MB
This is a test to check for heart muscle damage or detect a recent heart attack.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test
CK-MB is one of three forms (isoenzymes) of the enzyme creatine kinase (CK). CK is released from muscle cells and is detectable in the blood whenever there is muscle damage. The small amount of CK that is normally in the blood is primarily CK-MM. CK-BB almost never gets into the blood, and CK-MB will typically only be present in significant amounts when the heart is damaged. A CK test measures the total level but does not distinguish between the three isoenzymes. When there is an increased amount of CK present in the blood, the CK-MB test can be used to determine whether it is due to heart damage or is more likely to be related to skeletal muscle injury.
40,000UGXCreatinine Kinase MB
40,000UGX -
COVID-19 Antigen Test (Rapid) in Kampala
This is a rapid test used to screen for Covid 19 infection when experiencing the typical Covid19 symptoms such as runny nose, headaches, general weakness, sore throat, chest pain among others. Test results will be ready in 6 hours.
Rocket Health doctors will call to share results and give medical advise.
If one tests positive, one may choose to enroll onto our COVID-19 home-based care program.
40,000UGXCOVID-19 Antigen Test (Rapid) in Kampala
40,000UGX -
BLOOD PREGNANCY TEST (HCG QUANTITATIVE)
A blood test that measures the quantity of hCG (human chorionic gonadotriphin) hormone in your blood and is used to confirm pregnancy.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform your doctor if you are on any medications or have any underlying medical conditions or allergies before undergoing this test.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced by the placenta of a pregnant woman. HCG can be detected in blood samples after 8-11 days of conception. The levels of HCG doubles continuously for every 48-72 hours and the peak levels can be observed during 8-11 weeks after conception.
45,000UGXBLOOD PREGNANCY TEST (HCG QUANTITATIVE)
45,000UGX -
LIPID PROFILE (Blood Cholestrol test)
This is a panel of blood tests used to measure the level of specific lipids like cholesterol, triglycerides in blood. Results can show approximate risk of heart disease.
Blood.
Inform your doctor if you are on any medications or have any underlying medical conditions or allergies before undergoing this test. For this test, fasting for at least 8 to 12 hours is recommended.
Lipids are a group of fats and fat-like substances that are important constituents of cells and sources of energy. Cholesterol and triglycerides are the two important lipids. Cholesterol and triglycerides are transported are circulated into the blood through lipoprotein particles. High-density lipoproteins (HDL) are considered as good cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) is considered as bad cholesterol. High-density cholesterol carries cholesterol to the liver from various parts of your body. LDL gets attached to the walls of arteries and clogs them. This leads to a condition called atherosclerosis.
45,000UGXLIPID PROFILE (Blood Cholestrol test)
45,000UGX -
RENAL FUNCTION TEST
This is a panel of blood tests that check if your kidneys are functioning well.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform your doctor if you are on any medications or have any underlying medical conditions or allergies before undergoing this test.
A group of tests that are performed together to evaluate kidney function. The tests measure levels of various substances, including several minerals, metabolites and electrolytes in the blood to determine the current health of your kidneys.
45,000UGXRENAL FUNCTION TEST
45,000UGX -
Glycosylated Haemoglobin test (HbA1c)
The hemoglobin A1c is a test that tells your average level of blood sugar over the past 2 to 3 months. It’s also called HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin test
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform your doctor if you are on any medications or have any underlying medical conditions or allergies before undergoing this test.
Hemoglobin A1c, also called A1c or glycated hemoglobin, is hemoglobin with glucose attached. The A1c test evaluates the average amount of glucose in the blood over the last 2 to 3 months by measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in the blood.
45,000UGXGlycosylated Haemoglobin test (HbA1c)
45,000UGX -
Free T3
This is a test used to evaluate the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and monitor thyroid treatment.
Blood.
Acute illness may affect thyroid testing test results. It is generally recommended that thyroid testing be avoided in hospitalized patients Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Triiodothyronine (T3) is one of two major hormones produced by the thyroid gland, the other major thyroid hormone is called thyroxine (T4) and together they help control the rate at which the body uses energy. If the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of T4 and T3, then the person affected may have symptoms associated with overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism), such as nervousness, tremors of the hands, weight loss, insomnia, and puffiness around dry, irritated eyes and in some cases, bulging eyes. Insufficient amounts of T4 and T3, then the person may have signs and symptoms associated with underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) and a slowed metabolism, such as weight gain, dry skin, fatigue, and constipation
45,000UGXFree T3
45,000UGX -
Free T4
This is a test used to evaluate the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and monitor thyroid treatment.
Blood.
If you take thyroid hormone as treatment for thyroid disease, it is recommended that your blood sample be drawn before you take your dose for that day. Acute illness may also affect thyroid testing results so it is generally recommended that thyroid testing be avoided in hospitalized patients. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Most of the hormone produced by the thyroid is T4. This hormone is relatively inactive, but it is converted into the much more active T3 in the liver and other tissues. If the thyroid gland does not produce sufficient T4 and T3 (underactive thyroid), due to thyroid dysfunction or to insufficient TSH, then the affected person experiences symptoms of hypothyroidism such as weight gain, dry skin, cold intolerance, irregular menstruation, and fatigue. If the thyroid gland produces too much T4 and T3, the affected person may experience symptoms associated with overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism), such as rapid heart rate, anxiety, weight loss, difficulty sleeping, tremors in the hands, and puffiness around dry, irritated eyes and in some cases, bulging eyes.
45,000UGXFree T4
45,000UGX -
Thyroid- Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
This is a blood test that measures the amount of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone in the blood.
Blood.
If you take thyroid hormone as treatment for thyroid disease, it is recommended that your blood sample be drawn before you take your dose for that day. Acute illness may also affect thyroid testing results so it is generally recommended that thyroid testing be avoided in hospitalized patients. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications including multivitamins and supplements, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
To help diagnose thyroid disorders and to monitor treatment of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism;sometimes a TSH test is used to screen newborns for congenital hypothyroidism.
45,000UGXThyroid- Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
45,000UGX