No products in the cart.
Best Seller Items
-
Benylin with codeine
Benylin Codeine Syrup helps you to clear dry and stubborn coughs, providing relief from persistant coughing
30,000UGXBenylin with codeine
30,000UGX -
Valupak Vitamin C Effervescent Tablets 1000mg 1 tin
AvaCare’s Simple Health Vitamin C contains 20 Orange Flavoured Effervescent Tablets.
AvaCare’s Effervescent Vitamin C has been designed so you get a massive boost of well-needed Vitamin C as vitamin C helps support the normal function of your Immune and Nervous Systems, giving your immune system an immediate boost. It can also help reduce the effects of Tiredness and Fatigue
30,000UGX -
Midazolam 7.5mg Dormicum tablets 10’s
Midazolam Tablet is a prescription medicine used as a sedative or for conscious sedation before diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. It relieves anxiety and muscle tensions, thus making the person comfortable before investigations or minor surgical or dental procedures.Some common side effects of this medicine include memory impairment, tiredness, depression, and confusion. It may cause dizziness
4,500UGX -
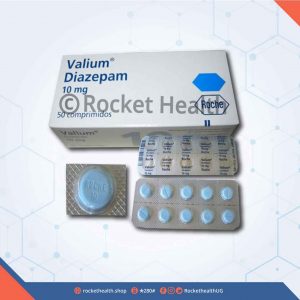
Diazepam 10mg Valium Tablets
Diazepam tablets is used to treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal and seizures. it is used to relieve muscle spasms and to provide sedation before medical procedures.
2,500UGXDiazepam 10mg Valium Tablets
2,500UGX -
COVIDEX (Pack of 5 bottles)
Get 5 units of COVIDEX at Ugx 65,000
Made by Jena Herbals Uganda Limited, Covidex is approved by NDA to be used as a supportive treatment for COVID-19 in Uganda
Ingredients
- Extract of Zanthoxylum gilletii (East African satinwood),
- Warbugia Ugandensis
- Sodium chloride
Mechanism of Action:
- Inhibits SARS CoV-2 Virus growth
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Immune modulatory effects
- Anti-hyperglycemic effects
Dose
- Adults: 6 drops in the mouth, 3 times a day.
- Children 5 – 12 years: 3 drops in the mouth, 3 times a day
- Children below 5 years: 1 drop in the mouth, 3 times a day
50,000UGXCOVIDEX (Pack of 5 bottles)
50,000UGX -
Sildenafil 50mg PENEGRA 50 Tablet 4’s
Penegra is used to treat erectile dysfunction (impotence) in men. This helps men to get or maintain an erection. It belongs to a group of medicines known as phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE 5) inhibitors. It works by increasing blood flow to the penis.
1,200UGX
-
Serum Crag
Serum Crag is a test that detects cryptococcal antigen (abbreviated “CrAg”) in blood, an indicator of cryptococcal meningitis infection.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Cryptococcal infection usually presents as meningitis, which is a swelling of the meninges,the tissues that protect the brain and spinal cord. It is caused by C. neoformans which enters the human body via the respiratory tract. Elimination of C. neoformans is through cell mediated immunity, with the participation of neutrophils, macrophages and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. In the face of immunodeficiency(HIV infection, pregnancy etc), control of the infection fails, the fungus may then disseminate to the central nervous system or other organs. Definitive diagnosis is confirmed by the culture of specimens, often the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or blood, and sometimes in respiratory secretions The condition requires hospitalization and treatment with the intravenous (IV) antifungal medication amphotericin B.
35,000UGXSerum Crag
35,000UGX -
Reticulocyte Count
A reticulocyte test determines the number and/or percentage of reticulocytes( Immature Red Blood Cells) in the blood and is a reflection of recent bone marrow function or activity.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, where blood-forming (hematopoietic) stem cells differentiate and develop, eventually forming reticulocytes and finally becoming mature RBCs. A variety of diseases and conditions i.e hemorrhage, hemolysis, bone marrow disorder, kidney disease can affect the production of new RBCs and/or their survival, in addition to those conditions that may result in significant bleeding. These conditions may lead to a rise or drop in the number of RBCs and may affect the reticulocyte count.
25,000UGXReticulocyte Count
25,000UGX -
Luitenising Hormone
This test measures the amount of luteinizing hormone in the blood. (LH) is a hormone associated with reproduction. Its stimulation of either ovary or testicles results in the release of an egg from the ovary (ovulation) in women or testosterone production in men.
Blood.
Early morning samples are preferred. A woman’s sample should be collected at specific times during her menstrual cycle. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
LH is produced by the pituitary gland. In women of childbearing age, several hormones (LH, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estrogen and progesterone) rise and fall in a specific sequence during each menstrual cycle. In men, LH stimulates Leydig cells in the testicles to produce testosterone. In infants and children, LH levels rise shortly after birth and then fall to very low levels. Results of an LH test are typically considered with results of other hormone tests, such as FSH, estrogens, and/or testosterone.
50,000UGXLuitenising Hormone
50,000UGX -
Hepatitis B Core Antibody
The test is used to find out whether you are having an active infection with the Hepatitis B virus (HBV).
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before your this test
Hepatitis B Virus has a central core and a surrounding envelope. Your immune system makes IgM antibodies to the core of HBV during the active stage of infection.The presence of anti-HBc indicates previous or ongoing infection with hepatitis B virus in an undefined time frame. IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (IgM anti-HBc): Positivity indicates recent infection with hepatitis B virus (<6 mos). Its presence indicates acute infection
50,000UGXHepatitis B Core Antibody
50,000UGX -
Free T4
This is a test used to evaluate the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and monitor thyroid treatment.
Blood.
If you take thyroid hormone as treatment for thyroid disease, it is recommended that your blood sample be drawn before you take your dose for that day. Acute illness may also affect thyroid testing results so it is generally recommended that thyroid testing be avoided in hospitalized patients. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Most of the hormone produced by the thyroid is T4. This hormone is relatively inactive, but it is converted into the much more active T3 in the liver and other tissues. If the thyroid gland does not produce sufficient T4 and T3 (underactive thyroid), due to thyroid dysfunction or to insufficient TSH, then the affected person experiences symptoms of hypothyroidism such as weight gain, dry skin, cold intolerance, irregular menstruation, and fatigue. If the thyroid gland produces too much T4 and T3, the affected person may experience symptoms associated with overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism), such as rapid heart rate, anxiety, weight loss, difficulty sleeping, tremors in the hands, and puffiness around dry, irritated eyes and in some cases, bulging eyes.
45,000UGXFree T4
45,000UGX -
Free T3
This is a test used to evaluate the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and monitor thyroid treatment.
Blood.
Acute illness may affect thyroid testing test results. It is generally recommended that thyroid testing be avoided in hospitalized patients Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Triiodothyronine (T3) is one of two major hormones produced by the thyroid gland, the other major thyroid hormone is called thyroxine (T4) and together they help control the rate at which the body uses energy. If the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of T4 and T3, then the person affected may have symptoms associated with overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism), such as nervousness, tremors of the hands, weight loss, insomnia, and puffiness around dry, irritated eyes and in some cases, bulging eyes. Insufficient amounts of T4 and T3, then the person may have signs and symptoms associated with underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) and a slowed metabolism, such as weight gain, dry skin, fatigue, and constipation
45,000UGXFree T3
45,000UGX -
Factor X (Stuart-Prower factor)
This test is part of a group of screening tests to find out which type of bleeding disorder you may have.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Coagulation factors are proteins circulating in the blood that are essential for proper blood clot formation. Coagulation factor tests measure the function of or sometimes the amount of these proteins in the blood. There are nine coagulation factor proteins that can be measured clinically Factor I, II, V, VII, IX, X, XI, XIII. These factors are referred to by a name or Roman numeral or both in some cases. When one or more of these factors are produced in too small a quantity, or are not functioning correctly, they can cause excessive bleeding.
200,000UGXFactor X (Stuart-Prower factor)
200,000UGX -
Factor IX (Antihemophilic factor B or Christmas factor)
This test is part of a group of screening tests to find out which type of bleeding disorder you may have.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Coagulation factors are proteins circulating in the blood that are essential for proper blood clot formation. Coagulation factor tests measure the function of or sometimes the amount of these proteins in the blood. There are nine coagulation factor proteins that can be measured clinically Factor I, II, V, VII, IX, X, XI, XIII. These factors are referred to by a name or Roman numeral or both in some cases. When one or more of these factors are produced in too small a quantity, or are not functioning correctly, they can cause excessive bleeding.
200,000UGX -
(Factor I) Fibrinogen
This test measures the amount of fibrinogen in the blood which is an important component in blood clotting process.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Coagulation factors are proteins circulating in the blood that are essential for proper blood clot formation. Coagulation factor tests measure the function of or sometimes the amount of these proteins in the blood. There are nine coagulation factor proteins that can be measured clinically Factor I, II, V, VII, IX, X, XI, XIII. These factors are referred to by a name or Roman numeral or both in some cases. When one or more of these factors are produced in too small a quantity, or are not functioning correctly, they can cause excessive bleeding.
200,000UGX(Factor I) Fibrinogen
200,000UGX -
Factor VII(Proconvertin)
This blood test evaluates the functioning of a protein that helps blood to clot.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Coagulation factors are proteins circulating in the blood that are essential for proper blood clot formation. Coagulation factor tests measure the function of or sometimes the amount of these proteins in the blood. There are nine coagulation factor proteins that can be measured clinically Factor I, II, V, VII, IX, X, XI, XIII. These factors are referred to by a name or Roman numeral or both in some cases. When one or more of these factors are produced in too small a quantity, or are not functioning correctly, they can cause excessive bleeding.
200,000UGXFactor VII(Proconvertin)
200,000UGX -
Factor V (Proaccelerin or labile factor)
This is a blood test that checks for a deficiency in a protein known as factor V that helps in blood clotting.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Coagulation factors are proteins circulating in the blood that are essential for proper blood clot formation. Coagulation factor tests measure the function of or sometimes the amount of these proteins in the blood. There are nine coagulation factor proteins that can be measured clinically Factor I, II, V, VII, IX, X, XI, XIII. These factors are referred to by a name or Roman numeral or both in some cases. When one or more of these factors are produced in too small a quantity, or are not functioning correctly, they can cause excessive bleeding.
200,000UGXFactor V (Proaccelerin or labile factor)
200,000UGX -
Factor IX
This test is part of a group of screening tests to find out which type of bleeding disorder you may have.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Coagulation factors are proteins circulating in the blood that are essential for proper blood clot formation. Coagulation factor tests measure the function of or sometimes the amount of these proteins in the blood. There are nine coagulation factor proteins that can be measured clinically Factor I, II, V, VII, IX, X, XI, XIII. These factors are referred to by a name or Roman numeral or both in some cases. When one or more of these factors are produced in too small a quantity, or are not functioning correctly, they can cause excessive bleeding.
200,000UGXFactor IX
200,000UGX -
Factor II (Prothrombin)
This test measures how much of a protein called factor II is in your blood. It can help find out whether you have a bleeding or blood clotting disorder.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
Coagulation factors are proteins circulating in the blood that are essential for proper blood clot formation. Coagulation factor tests measure the function of or sometimes the amount of these proteins in the blood. There are nine coagulation factor proteins that can be measured clinically Factor I, II, V, VII, IX, X, XI, XIII. These factors are referred to by a name or Roman numeral or both in some cases. When one or more of these factors are produced in too small a quantity, or are not functioning correctly, they can cause excessive bleeding.
200,000UGXFactor II (Prothrombin)
200,000UGX -
Creatinine Kinase MB
This is a test to check for heart muscle damage or detect a recent heart attack.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test
CK-MB is one of three forms (isoenzymes) of the enzyme creatine kinase (CK). CK is released from muscle cells and is detectable in the blood whenever there is muscle damage. The small amount of CK that is normally in the blood is primarily CK-MM. CK-BB almost never gets into the blood, and CK-MB will typically only be present in significant amounts when the heart is damaged. A CK test measures the total level but does not distinguish between the three isoenzymes. When there is an increased amount of CK present in the blood, the CK-MB test can be used to determine whether it is due to heart damage or is more likely to be related to skeletal muscle injury.
40,000UGXCreatinine Kinase MB
40,000UGX -
Carcino Embryonic Antigen (CEA)
A carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) test is a blood test used to help diagnose and manage certain types of cancers during treatment.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test
CEA may be produced by the cancer cells. CEA may then be detected in blood, but it will not indicate which kind of cancer is present. CEA is often used to monitor patients with cancers of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract such as bowel (colorectal) cancer. It may be raised in other cancers, such as ovarian and breast cancers, but can also be raised in benign conditions such as liver disease and inflammatory bowel disease (Crohns disease or ulcerative colitis).
90,000UGXCarcino Embryonic Antigen (CEA)
90,000UGX -
CA-125 (Ovarian cancer)
A Cancer Antigen 125 test measures the amount of the protein cancer antigen 125 in your blood helping to monitor ovarian cancer during and after treatment.
Blood.
No specific patient preparation protocol required. Inform the doctor if you are on any medications, have any allergies or underlying medical conditions before this test.
CA 125 is a protein often found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells and in some normal tissues. It is used as a marker for ovarian cancer. However, CA 125 levels may also be high in other types of non-cancerous conditions, including menstruation, pregnancy, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
75,000UGXCA-125 (Ovarian cancer)
75,000UGX